Publications
"Network Learning Approaches to study World Happiness"
Arxiv Pre-Print
The United Nations in its 2011 resolution declared the pursuit of happiness a fundamental human goal and proposed public and economic policies
centered around happiness. In this paper we used 2 types of computational strategies viz. Predictive Modelling and Bayesian Networks (BNs) to
model the processed historical happiness index data of 156 nations published by UN since 2012. We attacked the problem of prediction using
General Regression Neural Networks (GRNNs) and show that it out performs other state of the art predictive models.
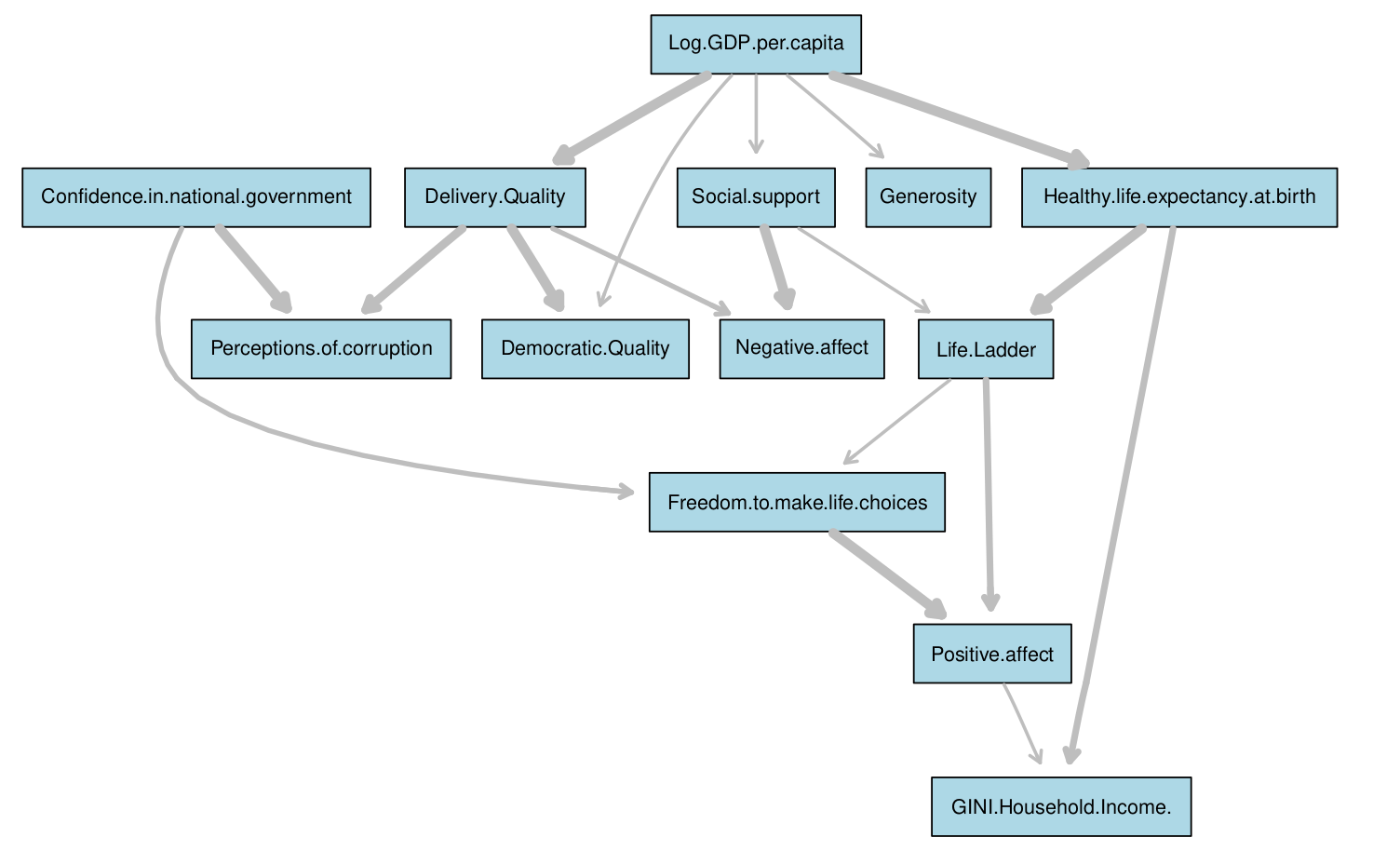
To understand causal links amongst key features that have been proven to have a significant impact on world happiness,
we first used a manual discretization scheme to discretize continuous variables into 3 levels viz. Low, Medium and High.
A consensus World Happiness BN structure was then fixed after amalgamating information by learning 10000 different BNs using bootstrapping.
Lastly, exact inference through conditional probability queries was used on this BN to unravel interesting relationships among the important
features affecting happiness which would be useful in policy making.
 Full Text
Code
Full Text
Code
"Machine Learning Approaches to Identify and Design Low Thermal Conductivity Oxides for Thermoelectric Applications"
in Data Centric Engineering- Cambrdige University Press (Aug'2020)
The search space for new thermoelectric oxides has been limited to the alloys of a few known systems, such as ZnO, SrTiO3
Notwithstanding the high power factor, their high thermal conductivity is a roadblock in achieving higher efficiency.
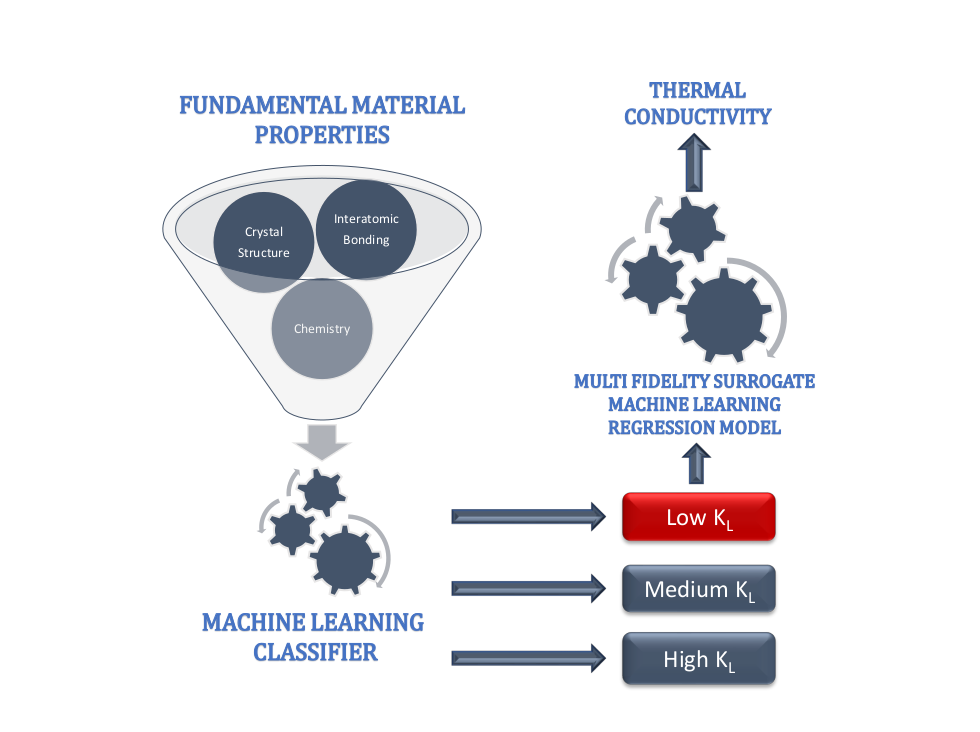
In this paper, we apply machine-learning models for discovering novel transition metal oxides with low lattice thermal conductivity (kL).
A two-step process is proposed to address the problem of small datasets frequently encountered in materials informatics.
First, a gradient boosted tree classifier is learnt to categorize unknown compounds into three categories of kL: Low, Medium, and High.
In the second step, we fit regression models on the targeted class (i.e. low kL) to estimate kL with an R2 > 0.9.
Gradient boosted tree model was also used to identify key material properties influencing classification of kL,
namely lattice energy per atom, atom density, band gap, mass density, and ratio of oxygen by transition metal atoms.
Only fundamental materials properties describing the crystal symmetry, compound chemistry and interatomic bonding were used in the classification process,
which can be readily used in the initial phases of materials design. The proposed two-step process addresses the problem of small datasets and
improves the predictive accuracy. The machine learning approach adopted in the present work is generic in nature and can be combined with
high-throughput computing for the rapid discovery of new materials for specific applications.
 Full Text
Code
Full Text
Code
"Get Bristol moving: tackling air pollution in Bristol city centre"
by Alan Turing Institute (April'2020)
Air quality is an increasing public health concern in UK cities, and Bristol is no exception breaching annual targets for nitrogen dioxide.
In Bristol, five people die each week as a result of poor air quality. Like most UK cities, in Bristol the main cause of air pollution is traffic.
To reduce the negative impacts of air pollution, and meet increasingly stringent European Union pollutant standards, Bristol is currently consulting
on a Clean Air Strategy. A range of policies is proposed including increased public transport, clean air zones and road closures.
The city council currently collects a wealth of data (about air quality, traffic flows and weather) for analyzing the distribution of air quality
and the relationship with various drivers. Such understanding has the potential to feed into the design and evaluation of air quality policies.
However, the council has limited capacity for analyzing and interpreting such large and complex datasets.
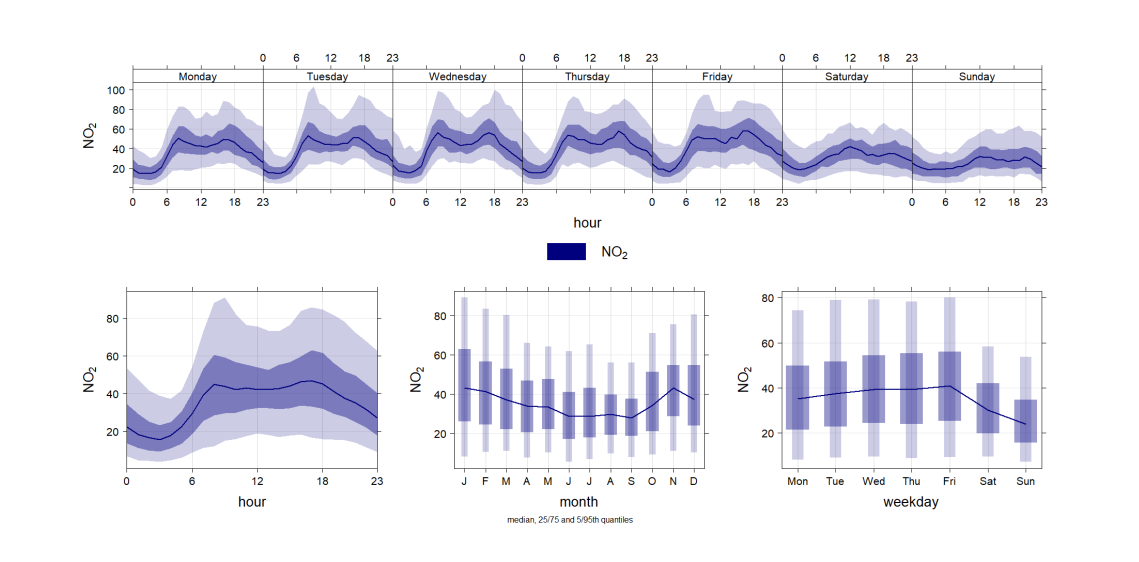
This project mines this data to understand both the spatial and temporal distribution of air quality. the driving factors of air pollution in different
parts of the city, with a particular focus upon traffic.
 Full Text
Code
Full Text
Code
 Full Text
Code
Full Text
Code
 Full Text
Code
Full Text
Code
 Full Text
Code
Full Text
Code